Reactor
什么是Reactor
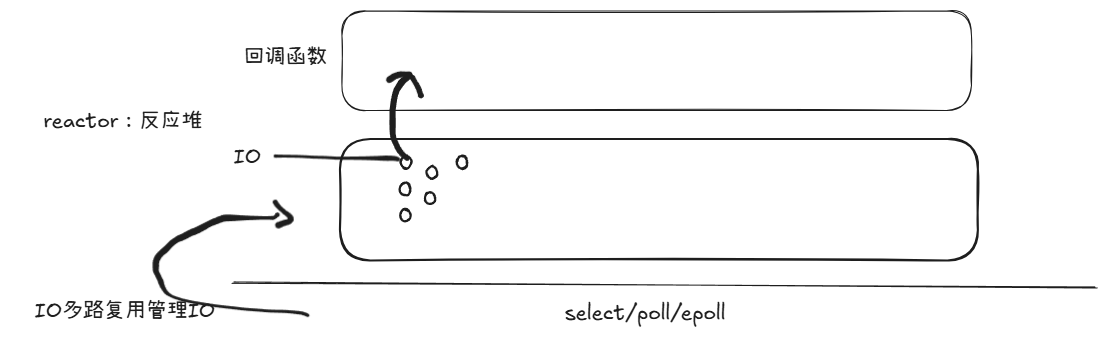
reactor用来关注网络中的事件,在处理网络的时候由网络IO的管理变为网络事件管理,其核心的思想就是通过回调函数来处理这些IO,也称为IO事件。每一个不同的IO事件调用不同的回调函数。
Reactor实现关注两点:
- event与callback的匹配。
- 每一个IO与之对应。
reactor这里是理解为一个反应堆,将某些IO转换成几类事件进行“注册”,再将这些事件通过回调函数进行处理。
下面实现的代码将这几类fd对应到EPOLL事件中,再分别写对应的回调函数来对事件进行处理
Reactor实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
#define CONNECTION_SIZE 1024
typedef int (*RCALLBACK)(int fd);
//声明
int recv_cb(int fd);
int send_cb(int fd);
int accept_cb(int fd);
int set_event(int fd, int state, int flag);
int epfd = 0;
struct conn{
int fd;
char rbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int rlength;
char wbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int wlength;
RCALLBACK send_callback;
union{
RCALLBACK recv_callback;
RCALLBACK accept_callback;
}r_action;
};
struct conn conn_list[CONNECTION_SIZE] = {0};
//listenfd(sockfd)-->EPOLLIN-->accept_cb
int accept_cb(int fd){
struct sockaddr_in clientaddr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(clientaddr);
int clientfd = accept(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&clientaddr, &len);
printf("accept finished %d\n", clientfd);
conn_list[clientfd].fd = clientfd;
conn_list[clientfd].r_action.recv_callback = recv_cb; //recv callback
conn_list[clientfd].send_callback = send_cb; //send callback
memset(&conn_list[clientfd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
conn_list[clientfd].rlength = 0;
memset(&conn_list[clientfd].wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
conn_list[clientfd].wlength = 0;
set_event(clientfd, EPOLLIN, 1);
return 0;
}
int recv_cb(int fd){
struct conn *c = &conn_list[fd];
int count = recv(fd, c->rbuffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0);
if(count == 0){ //disconnect
printf("client disconnect %d\n",fd);
close(fd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL);
return 0;
}
c->rlength = count;
printf("RECV: %s\n",c->rbuffer);
c->wlength = c->rlength;
memcpy(c->wbuffer, c->rbuffer, c->wlength);
set_event(fd, EPOLLOUT, 0);
return count;
}
int send_cb(int fd){
struct conn *c = &conn_list[fd];
int count = send(fd, c->wbuffer, c->wlength, 0);
set_event(fd, EPOLLIN, 0);
return count;
}
int init_server(unsigned short port){
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
//存储服务器地址与端口号的结构体
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);// 0.0.0.0
servaddr.sin_port = htons(2000);
if(-1 == bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&servaddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr))){
printf("bind failed: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
listen(sockfd,10);
printf("listen finished %d\n",sockfd);
return sockfd;
}
int set_event(int fd, int state, int flag){
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = state;
ev.data.fd = fd;
if(flag){
return epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev);
}else{
return epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, &ev);
}
}
int main(){
unsigned short port = 2000;
int sockfd = init_server(port);
epfd = epoll_create(1);
conn_list[sockfd].fd = sockfd;
conn_list[sockfd].r_action.accept_callback = accept_cb; //accept callback
set_event(sockfd, EPOLLIN, 1);
while(1){ //mainloop
struct epoll_event events[1024] = {0};
int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1); //blocking
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < nready; i++){
int connfd = events[i].data.fd;
//accept
if(events[i].events & EPOLLIN){
conn_list[connfd].r_action.recv_callback(connfd);
}
if(events[i].events & EPOLLOUT){
conn_list[connfd].send_callback(connfd);
}
}
}
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权