线程池
线程池
线程池的使用场景:
服务器连接通信
- 在服务器与客户端建立连接进行通信的时候,需要用到多线程进行,如果客户端有10万个,则按照普通做法,即一客户端一线程,需要开10万个线程,而在posix标准的线程,一个有8M,则16G内存只有2048个线程可开,故引出了线程池。
日志文件
- 磁盘操作远远比内存操作慢很多,在写线程的时候,会引起线程的挂起。故在落盘即执行写操作时与如何写, 这两个问题分开,如何写即是任务,执行写操作即是执行。
线程池的好处:
避免线程太多,使得内存耗尽。
避免线程创建与销毁的代价。
任务与执行分离。
线程池的基本原理:
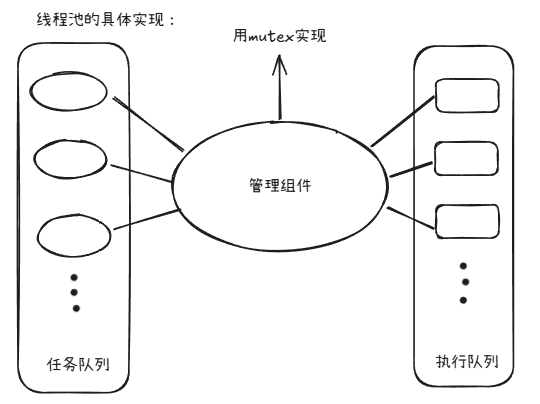
一个任务队列与一个执行队列,中间一个管理组件。
管理组件中有这两个队列与一个mutex锁,其中还有一个条件变量,这个条件变量的作用是
来使执行队列进行。
线程池即可以理解为上图中的管理组件。
故线程池需要定义三个东西,定义如下:
1.任务队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
struct nTask{
/* data */
void (*task_func) (struct nTask *task);
void *user_data;
struct nTask *prev;
struct nTask *next;
};
2. 执行队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
struct nWorker{
pthread_t thread_id;
int terminate;
struct nManager *manager;
struct nWorker *prev;
struct nWorker *next;
};
3.管理模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
typedef struct nManager{
struct nTask *tasks;
struct nWorker *workers;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}ThreadPool;
API定义
1
所需要提供给用户的API主要有以下功能,创建一个线程池,销毁一个线程池,往线程池里添加任务。
1. 创建线程池
这里面做两件事情,一个是激活执行队列中的“工人”,二是去任务队列里取任务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
int nThreadPoolCreate(ThreadPool *pool,int numWorkers){
//创建线程池,首先初始化各个参数
if(pool == NULL) return -1;
//工人必须大于等于1,执行队列里一定有一个工人。
if(numWorkers < 1) numWorkers = 1;
//初始化线程池,此处是静态初始化条件变量
memset(pool,0,sizeof(ThreadPool));
pthread_cond_t blank_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->cond, &blank_cond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutex, NULL);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < numWorkers; i++){
struct nWorker *worker = (struct nWorker*)malloc(sizeof(struct nWorker));
if(worker == NULL){
perror("malloc");
return -2;
}
memset(worker,0,sizeof(struct nWorker));
worker->manager = pool;
// INFO("nthreadpool worker %d start/n",i);
int ret = pthread_create(&worker->thread_id,NULL,nThreadPoolCallback,worker);
if(ret){
perror("pthread_create");
free(worker);
return -3;
}
LIST_INSERT(worker,pool->workers);
}
return 0;
}
其中LIST_INSERT是通过宏定义的函数,即链表的插入操作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
#define LIST_INSERT(item, list) do{ \
item->prev = NULL; \
item->next = list; \
if((list) != NULL) (list)->prev = item; \
list = item; \
}while(0)
2.线程回调函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
static void *nThreadPoolCallback(void *arg){
struct nWorker *worker = (struct nWorker*)arg;
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->manager->mutex);
//等待任务的到来
while(worker->manager->tasks == NULL){
//循环退出条件
if(worker->terminate) break;
//线程阻塞
pthread_cond_wait(&worker->manager->cond,&worker->manager->mutex);
}
if(worker->terminate){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->manager->mutex);
break;
}
//有任务就取出任务
struct nTask *task = worker->manager->tasks;
//从头取出一个节点
LIST_REMOVE(task,worker->manager->tasks);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->manager->mutex);
task->task_func(task);
}
free(worker);
}
这其中的LIST_REMOVE也是通过宏定义的函数,即链表的删除操作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
#define LIST_REMOVE(item, list) do{ \
if(item->prev != NULL) item->prev->next = item->next; \
if(item->next != NULL) item->next->prev = item->prev; \
if(list == item) list = item->next; \
item->prev = item->next = NULL; \
}while(0)
3.销毁线程池
其中要做的就是切断work结构体与task结构体的联系,并将线程回调函数终止。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
int nThreadPoolDestory(ThreadPool *pool,int nWorker){
struct nWorker *worker = NULL;
for(worker = pool->workers; worker != NULL; worker = worker->next){
worker->terminate = 1;
}
//这里加锁的原因是防止在广播时有些还未进行wait的即将进行wait的条件都一起满足!!!!
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
//唤醒所有线程,叫醒正在睡觉的员工,叫他们下班。
pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
pool->workers = NULL;
pool->tasks = NULL;
}
4.向线程池中添加任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
int nThreadPoolPushTask(ThreadPool *pool,struct nTask *task){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
LIST_INSERT(task,pool->tasks);
//唤醒一个线程
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权